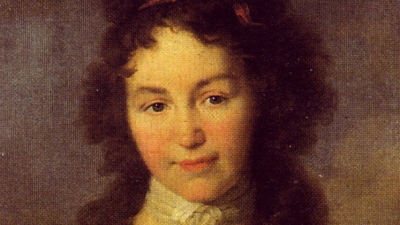
Caroline Schelling (‘Caroline’) wrote the fourth letter of hers that survives (the ‘4th Letter’) on October 7, 1778, shortly after she had turned 15, to a girl she met at boarding school who was to become her lifelong friend (Luise). The intensity of her friendship with Luise is evident already in the 4th Letter, for she tells Luise that in writing to her she “portrays her entire soul.” What prompted such depth of feeling for this letter relates not just to a significant moment in Caroline’s life but in every person’s life. In the second paragraph she refers to what was most likely her first sexual relationship. Given that context, Caroline demonstrates remarkable emotional maturity and intellectual sophistication in how she expresses herself.
She begins by referring to the “sensations of my heart,” telling Luise how she struggles to find “adequate words” to express them. She is not, she proudly insists, an “enthusiast” who simply gives into feelings, insisting instead on the importance of “going over” (Überlegung) them herself. Though Caroline was not taught Latin, it seems as if she had been taught the relevance to German of a Latin treatise from the 4th century CE on the method for defining words. Caroline’s ‘going over’ her feelings before writing Luise is consistent with its methodology: first, to confront the question of whether something even exists (an sit, Existenz) and then determining, to the extent possible, what it is (quid sit, Wesen) and what its qualities are (quale sit, Eigenschaften)–i.e., its relationship to other words (grammar) and hence how it can be communicated.
This methodology, which is applicable to a wide range of disciplines (e.g., legal argumentation, psychiatric diagnosis), is also analogous to a language theory Charles Segal argued is implicit in what remains of the writings of the 5th century BCE Sicilian Gorgias, a theory Segal related to Sappho’s poetry. That is relevant, because given the failed sexual relationship about which Caroline writes to Luise, the 4th Letter bears comparison to two poems by Sappho (S. 31 and S. 1) that Caroline surely then knew in translation. Caroline’s “sensations of my heart” is directly comparable to the palpitations of the heart Sappho refers to in the second stanza of S. 31. The immediate effects are comparable; Sappho cannot speak and Caroline cannot find “adequate words.” Though S. 31 appears to break off, S. 1 can be read as a continuation of it. There Sappho prays for divine intervention (Aphrodite) to deal with a failed sexual relationship; the closing prayer of its final stanza is analogous to the last sentence of the 4th Letter’s first paragraph: “Lord, you who know my heart . . . fulfill no wishes that are not pleasing to you, I am depending on you!”
In each case it would seem the answer is anticipated to be one that is not heard or read but rather felt in the heart, intuitively understood as the center point of all bodily feelings. That would be not an abstraction from the senses but an inward intensification of them. Such intensification becomes the basis for its outward expression not just in words, but in all forms of art.
Caroline grew up during a time of renewed interest in ancient Greek art and particularly nude sculpture, which rightly can be taken to symbolize the belief in the sacredness of the entire human body (a belief that correlates with heart centeredness). It is notable that the floruit of such sculpture predates Plato by almost a century and quite literally embodies principles utterly antithetical to his philosophy. It is also analogous to another art form that predates him and that he disparaged: reciting poetry (whether or not incorporated into a theatrical production). Poetic recitation requires fully identifying with the poet and poem to such a degree that it can be thought of as internalized sculpting.
The principles underlying sculpture and recitation are thus similar and of general applicability. Caroline, who enjoyed (and was appreciated for) reciting poetry, makes the point in a review she wrote of a book of essays on artistic appreciation (the “Review”). To judge art, she says, it is necessary to penetrate “deeply into the meaning and sensibility of both it and its initiator . . . surrendering oneself in quiet reflection to a disposition of loving, receptive observation . . . [to be] transpose[d] . . . into the world of the poet or artist.” She defends the book’s use of a fictional friar to voice religious reverence for art, effectively equating artistic appreciation with religious devotion, since it is only from feeling the divine within (i.e., internalizing god as the artist) that the divine outside is to be understood.
This was not something new for Caroline, as is evident from the 4th Letter that was written nearly twenty years before the Review. Not only does she seem to have internalized Sappho, but the opening line of S. 31 (a man, “equal to the gods”) and the closing line of S. 1 (“my comrade,” the goddess) arguably encouraged her transition in the 4th Letter’s first paragraph from describing her feelings to Luise (psychology) to praying to God (theology). That transition anticipates the identification of psychology with theology Caroline articulates in the Review.
The remote antiquity of this identification and its association with goddess worship to which Sappho attests, as well as the recognition of it by Caroline at such a young age deserve attention, for it has quite a history, especially in German culture. Goethe quoted two lines of a 1st century CE Latin poem on astrology that essentially echo it in the guestbook atop Mount Brocken on September 4, 1784: who is able to know heaven except by a gift from heaven, who finds god unless a part of the gods is within them. It is not known when Caroline met Goethe; it has been speculated that he was the father of her first daughter, Auguste, born April 28, 1785. In August 1784 Caroline was living in a mining town not far from Brocken.
The opening paragraph of an essay published by Caroline’s third husband in 1809, only months before her death, contains a reference to the principle of knowing the god outside from the god within, correctly noting that its connection with Empedocles proves it predates Plato. In 1936 Heidegger characterized that essay as “one of the most profound works” of Western philosophy. In my next post(s) I hope to show that its profundity relates to a critique of Plato (and other philosophers) that derives from Caroline and her appreciation of ancient Greek female spirituality, and not to glorifying supermen.
 Stuart Dean has a B.A. (Tulane, 1976) and J.D. (Cornell, 1995) and is currently an independent researcher and writer living in New York City. He has studied, practiced and taught Tai Chi, Yoga and related disciplines for over forty years. Stuart has a blog on Sappho and the implications of her poetry for understanding the past, present and future: http://studysappho.blogspot.com/
Stuart Dean has a B.A. (Tulane, 1976) and J.D. (Cornell, 1995) and is currently an independent researcher and writer living in New York City. He has studied, practiced and taught Tai Chi, Yoga and related disciplines for over forty years. Stuart has a blog on Sappho and the implications of her poetry for understanding the past, present and future: http://studysappho.blogspot.com/



 How much longer do I as a Muslim American female, have to deal with the “gang-buster,” terrorizing, “Satan” worshipers high-jacking my faith for the sake of trying to supposedly ‘preserve’ it? Who are these wackos and why do they seem to represent my faith in mainstream media? Where did they all come from? Which terrorist schools have they all graduated from and what truly is their agenda?
How much longer do I as a Muslim American female, have to deal with the “gang-buster,” terrorizing, “Satan” worshipers high-jacking my faith for the sake of trying to supposedly ‘preserve’ it? Who are these wackos and why do they seem to represent my faith in mainstream media? Where did they all come from? Which terrorist schools have they all graduated from and what truly is their agenda? It is heartening to hear the many condemnations Muslim scholars have issued of ISIS and its methods and actions. One of the latest attempts comes in the form of an open
It is heartening to hear the many condemnations Muslim scholars have issued of ISIS and its methods and actions. One of the latest attempts comes in the form of an open  Today I am honored to give a lecture on “Queering Iconography: Holy Women Icons from Sappho to Pauli Murray” at the
Today I am honored to give a lecture on “Queering Iconography: Holy Women Icons from Sappho to Pauli Murray” at the 


